LLM Optimization via Synthetic Distillation
Utilizing functional specialization to benefit from smaller models in the absence of training data
The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to new learning techniques like K-shot prompting, where a model that is given just a few question-and-answer examples can create new answers for novel questions. This works best on large models, but running them can be expensive and slow. Here we will demonstrate how to use Model Distillation to use the outputs of a larger model to train a smaller model in order to achieve comparable performance with less computational weight.
Understanding Model Distillation
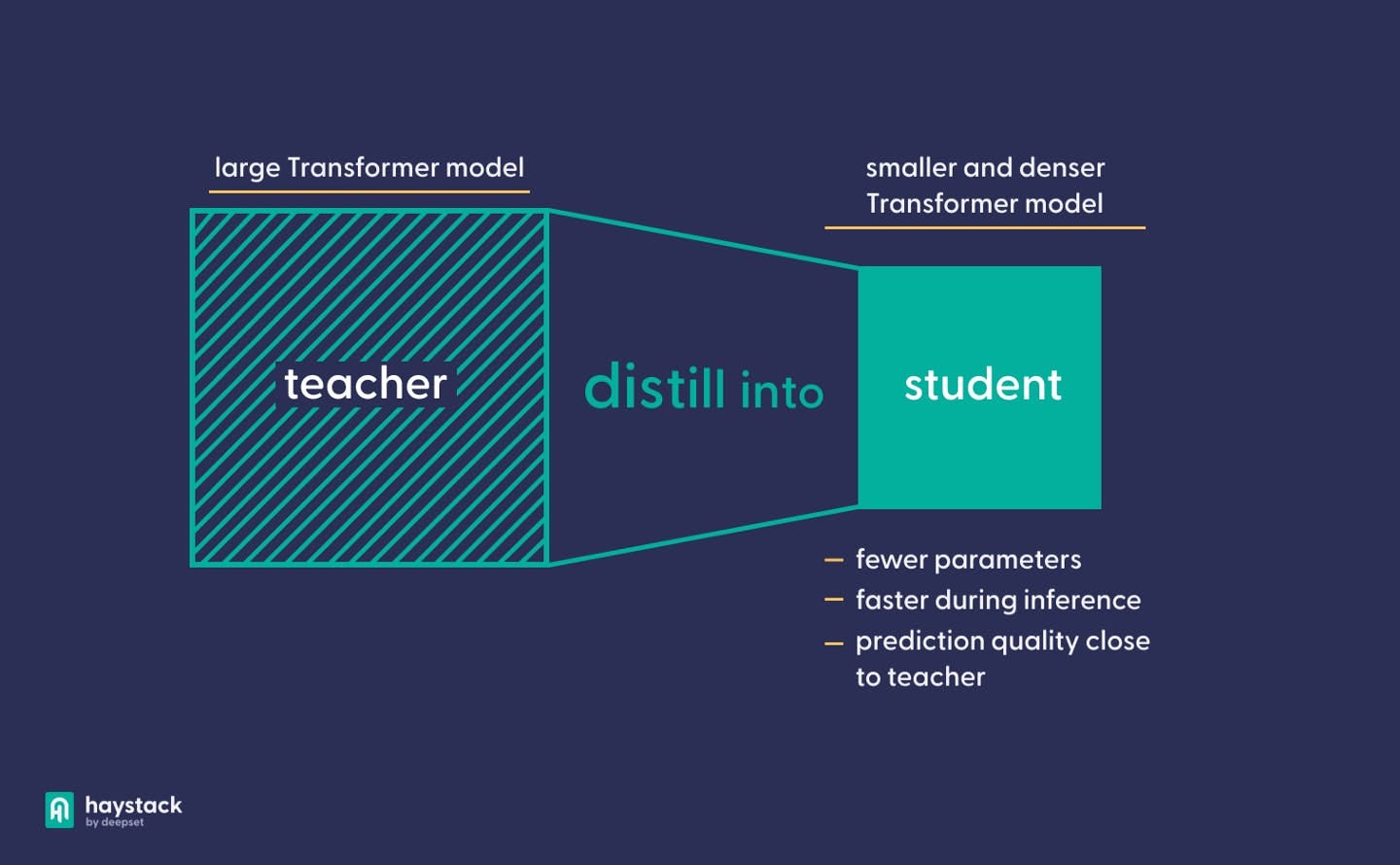
Model distillation transfers knowledge from a larger "teacher" model to a smaller, efficient "student" model, aiming for the student to mimic the teacher's outputs with fewer resources. In our examples, we’ll use the ChatGPT-4 as the teacher, and the 70-million parameter pythia-70m model as the student. We’ll also compare the performance with the 3-billion parameter open-llama model as a student. In principle, you can use any two models.
Model Distillation Diagram (cred: deepset.ai)
Setup
Let’s say we’re going to use our LLMs to help us create a list of subtasks from a larger task. For example, breaking down how to find all 2-bedroom apartments within a 5-mile radius of the San Jose station. First, we’ll need to give our teacher model an example of how to do this.
We prompt our parent LLM with 4 elements, 3 for our seed prompt + our question:
Our goal (split a task into subtasks)
An example question (find certain emails)
An example answer (steps to find those emails)
The question we want the LLM to answer (the apartment search)
Prompt:
Split Q into the subtasks that are needed to execute it. Separate each subtask with a comma.
Q: Delete all the emails sent more than 5 years ago to my old company.
A: Find all emails sent 5 years ago, find what was the email of the old company, find which emails from 5 years ago were sent to that email, Delete those emails.<END>
Q: What are all the apartments in San Jose that are five miles away from the train station and have two bedrooms?
Response:
What is the train station, What are all the apartments within 5 miles of that address, Find which of those apartments have two bedrooms.<END>
K-Shot Prompting: Teacher vs Student
We have just used K-shot prompting to “train” the teacher LLM how to answer certain types of questions. K stands for the number of examples given during training, so in this case with only one example, we have used 1-shot prompting. If we were to use 1-shot prompting with the much smaller student LLM, it would be unlikely to perform nearly as well, with an answer that is less accurate or coherent (see Results section for a more in-depth comparison).
We would still like to use our more lightweight student LLM, since it will be quicker and cheaper to run, so we’ll use model distillation to improve its answers.
Data Synthesis and Distillation Pipeline
Start with a prompt that includes a single shot example in its context window and a task that we want to split. We’ll call this the “seed prompt.”
Get the large LLM’s completion of the seed prompt (this will be a comma-separated list of subtasks).
Using the task contained in the seed prompt, generate 200 similar tasks using a large LLM (ChatGPT in this case). Then use the 1-shot context with each of these tasks to get 200 (task, subtask list) pairs. This step is called data synthesis- we create a dataset for a small LLM to finetune on using a single prompt to the big LLM. Note that every run of data synthesis, even with the same seed prompt, will likely result in non-identical datasets.
We finetune our small LLM using the 200 pairs for 100 epochs.
For evaluation on distillation quality, we compare the semantic similarity of the distilled model’s outputs to the output that the big LLM generated using 1-shot prompting.
Results
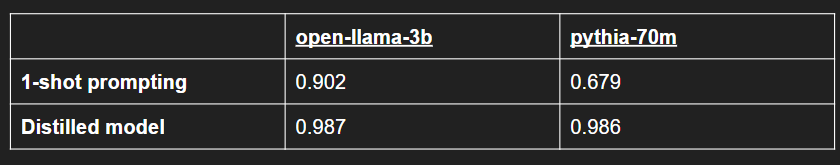
For the large LLM we used ChatGPT (using gpt-4). We distilled 2 small LLMs, open-llama-3b and pythia-70m. The figures on the table indicate the semantic similarity of the subtask list generated by a small LLM to the subtask list generated by ChatGPT for the same input task. We consider the subtask list generated by ChatGPT to be the ground truth. The distilled models require no k-shot examples, and are simply provided the task we want to split.
We assembled two different test sets using the same data synthesis technique we used to make the training set. The first test set was created using the same seed prompt as the training set, the second was created using a different seed prompt.
Table 1, 50 datapoint test set (same seed prompt as training set):
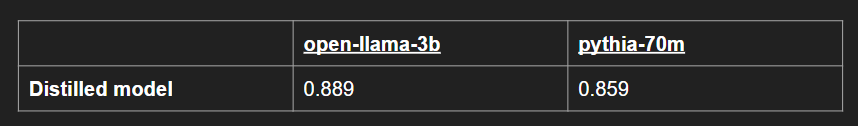
Table 2, 50 datapoint test set (different seed prompt as training set):
Analysis
We can see in Table 1 that the tiny 70 million parameter Pythia model does not have too much success with 1-shot prompting. The 3 billion parameter open-llama model does decently with 1-shot prompting, however, it is 43 times larger than Pythia. Both models are significantly smaller than ChatGPT. Using distillation and our data synthesis technique, both open-llama and Pythia had significant improvements in performance.
Table 2 shows performance of a test set with a different seed prompt. This furthers the delta between the training and testing datasets. The distilled Pythia model still greatly outperformed its baseline, while the open-llama model did slightly worse. This shows that for prompts that are very different from the prompts that open-llama was distilled on, it is better to use a baseline open-llama model with 1-shot prompting. However, for the tiny Pythia model, the distilled model had a greatly increased ability to task split. With this distillation technique, we have shown how we can take an LLM several orders of magnitude smaller than ChatGPT, and make it perform a specific subtask at a comparable level.
Code
We implemented this technique using Anarchy’s LLM-VM as follows:
from llm_vm.client import Client
client = Client(big_model='chat_gpt', small_model='pythia')
response = client.complete(prompt = 'Q: What are all the apartments in San Jose that are five miles away from the train station and have two bedrooms?',
context='
Split Q into the subquestions that are needed to answer it. Seperate each subquestion with a comma.
Q: Delete all the emails sent more than 5 years ago to my old company.
A: Find all emails sent 5 years ago, find what was the email of the old company, find which emails from 5 years ago were sent to that email, Delete those emails.<END>',
openai_key=settings.openai_api_key,
finetune = True, data_synthesis = True")